Learning Outcomes
i. Understand the concept of natural selection and its role in evolution.
ii. Recognize how variation within a population leads to differential survival.
iii. Explain why the best-adapted individuals are more likely to reproduce and pass on their genes.
i. Natural Selection: The Engine of Evolution
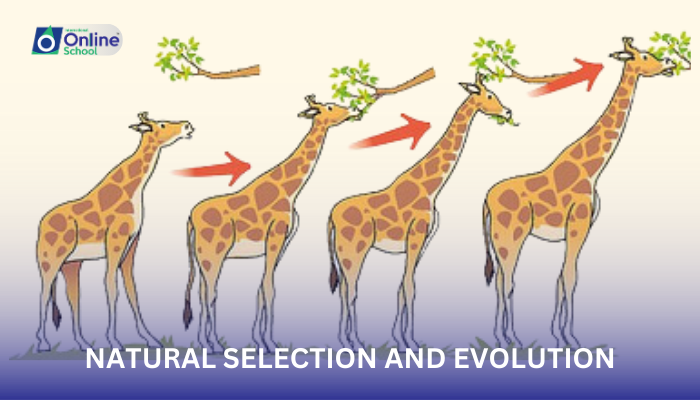
Natural selection is a mechanism of evolution proposed by Charles Darwin. It posits that individuals within a species show variation in physical traits, and these variations can influence an individual's ability to compete, survive, and reproduce in their environment. The fundamental idea is that individuals with traits better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and have more offspring, a concept known as "survival of the fittest."
ii. Variation and Competition Within Populations
In any given population, variation occurs naturally due to mutations, sexual reproduction, and other genetic processes. These variations can affect an organism's ability to obtain resources like food, shelter, and mates. As resources are often limited, this leads to competition among individuals. Traits that confer a competitive edge can lead to better survival rates.
iii. Differential Survival and Reproduction
Differential survival is the concept that some individuals are more likely to survive to reproductive age than others, based on their genetic traits. Those that survive and are more "fit" in terms of Darwinian fitness (reproductive success) will have more opportunities to reproduce. As a result, their genes are more likely to be passed on to the next generation.
iv. The Best-Adapted Individuals
The best-adapted individuals are those whose traits are best suited for their environment. For instance, a moth with a wing coloration that helps it avoid predation is more likely to survive and reproduce than a moth that is easily seen by predators. Over time, the genes that contribute to the beneficial trait will become more common in the population.
v. The Outcome of Natural Selection
The outcome of natural selection is a population that is better adapted to its specific environment. This process can lead to evolutionary changes within the population and, given sufficient time and isolation, the emergence of new species. However, if the environment changes, different traits may be favored, leading to new evolutionary paths.
In conclusion, natural selection is a fundamental principle of evolutionary biology. It explains how genetic variation within a population can result in individuals with certain advantageous traits having better survival and reproductive success, leading to the propagation of these traits in future generations. This process drives the evolution of species and the diversity of life forms observed on Earth.